Mac Os X 10.5 8 Combo Update Download UPDATED
Mac Os X 10.5 8 Combo Update Download
| A version of the macOS operating system | |
 | |
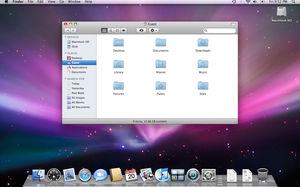 Screenshot of Mac OS X Leopard. Note how the Dock and window designs are dissimilar from previous versions of Mac Bone X. | |
| Developer | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Os family | |
| Source model | Closed, with open source components |
| Released to manufacturing | October 26, 2007 (2007-10-26) [two] |
| Latest release | ten.5.8 (Build 9L31a) [3] / August xiii, 2009 (2009-08-13) [4] |
| Update method | Apple Software Update |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, PowerPC |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (XNU) |
| License | Commercial proprietary software [5] with Apple tree Public Source License (APSL) |
| Preceded past | Mac OS X 10.four Tiger |
| Succeeded by | Mac Bone X 10.6 Snow Leopard |
| Official website | Apple - Mac Bone X Leopard at the Wayback Machine (archived May 28, 2009) |
| Back up status | |
| Unsupported every bit of well-nigh June 23, 2011, Safari support and iTunes back up terminated equally of 2012 every bit well. [6] [vii] | |
Mac Os X Leopard (version 10.5) is the sixth major release of macOS, Apple tree's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on Oct 26, 2007 as the successor of Mac Bone X 10.4 Tiger, and is available in two editions: a desktop version suitable for personal computers, and a server version, Mac OS 10 Server. It retailed for $129 [2] for the desktop version and $499 for Server. [viii] Leopard was superseded past Snowfall Leopard (version 10.6) in 2009. Leopard is the final version of macOS to support the PowerPC compages as Snow Leopard functions solely on Intel based Macs.
According to Apple, Leopard contains over 300 changes and enhancements compared to its predecessor, Mac Bone X Tiger, [ix] covering core operating system components too every bit included applications and developer tools. Leopard introduces a significantly revised desktop, with a redesigned Dock, Stacks, a semitransparent card bar, and an updated Finder that incorporates the Cover Flow visual navigation interface start seen in iTunes. Other notable features include support for writing 64-bit graphical user interface applications, an automatic backup utility called Fourth dimension Machine, back up for Spotlight searches across multiple machines, and the inclusion of Front end Row and Photo Booth, which were previously included with only some Mac models.
Apple missed Leopard's release fourth dimension frame as originally announced by Apple tree's CEO Steve Jobs. When first discussed in June 2005, Jobs had stated that Apple intended to release Leopard at the end of 2006 or early 2007. [x] A year later, this was amended to Spring 2007; [eleven] however, on April 12, 2007, Apple issued a statement that its release would be delayed until October 2007 considering of the development of the iPhone. [12]
New and changed features [ edit ]
Terminate-user features [ edit ]
Apple advertised that Mac Bone Ten Leopard has 300+ new features, [ix] including:
- A new and improved Automator , with easy starting points to easily beginning a workflow. Information technology likewise tin can quickly create or edit workflows with new interface improvements. At present information technology can employ a new action called "Watch Me Do" that lets you lot record a user action (similar pressing a push or decision-making an application without congenital-in Automator support) and replay as an action in a workflow. It can create more than useful Automator workflows with deportment for RSS feeds, iSight camera video snapshots, PDF manipulation, and much more than.
- Back to My Mac , a feature for MobileMe users that allows users to access files on their home computer while abroad from home via the internet.
- Boot Camp , a software assistant allowing for the installation of other operating systems, such as Windows XP (SP2 or later on) or Windows Vista, on a separate partition (or separate internal bulldoze) on Intel-based Macs.
- Dashboard enhancements, including Web Prune, a feature that allows users to plough a part of any Spider web page displayed in Safari into a live Dashboard widget, and Dashcode to help developers lawmaking widgets. [thirteen]
- New Desktop, comprises a redesigned three-D dock with a new group feature chosen Stacks , which displays files in either a "fan" manner, "grid" mode, or (since 10.5.ii) a "list" style. Rory Prior, on the ThinkMac web log, criticized the shelf-like Dock along with a number of other changes to the user interface. [14]
- Lexicon can at present search Wikipedia, and a lexicon of Apple terminology as well. Besides included is the Japanese-language dictionary Daijisen, Progressive E-J and Progressive J-E dictionaries, and the 25,000-discussion thesaurus Tsukaikata no Wakaru Ruigo Reikai Jiten ( 使い方の分かる類語例解辞典 ), all of which are provided by the Japanese publisher Shogakukan. [xv] [ix]
- A redesigned Finder , with features similar to those seen in iTunes 7, including Cover Flow and a Source list-like sidebar.
- Front Row has been reworked to closely resemble the interface of the original Apple TV.
- iCal calendar sharing and grouping scheduling as well as syncing effect invitations from Mail. [16] The icon also reflects the electric current date even when the application is not running. In previous versions of Mac OS 10, the icon would show July 17 in the icon any time the application was not running merely the current date when the application was running.
- iChat enhancements, including multiple logins, invisibility, animated icons, and tabbed chats, similar to features present in Pidgin, Adium and the iChat plugin Chax; iChat Theater, allowing users to incorporate images from iPhoto, presentations from Keynote, videos from QuickTime, and other Quick Look features into video chats; and Backdrops, which are like to chroma keys, simply use a real-fourth dimension difference matte technique which does not require a green or blueish screen. iChat also implements screen sharing, a feature previously available with Apple tree Remote Desktop. [eleven] [17] [18]
- Mail enhancements including the additions of RSS feeds, Stationery, Notes, and to-dos. To-dos apply a system-broad service that is available to all applications. [xix]
- Network file sharing improvements include more granular control over permissions, consolidation of AFP, FTP and SMB sharing into one control panel, and the ability to share individual folders, a characteristic that had not been available since Mac Os nine. [20]
- Parental controls now include the power to identify restrictions on use of the Internet and to set parental controls from anywhere using remote setup. [21]
- Photo Booth enhancements, including video recording with real-time filters and bluish/green-screen applied science.
- Podcast Capture , an application allowing users to record and distribute podcasts. It requires access to a computer running Mac Os Ten Server with Podcast Producer.
- Preview adds support for annotation, graphics, extraction, search, markup, Instant Alpha and size adjustment tools. [22]
- Quick Look , a framework assuasive documents to be viewed without opening them in an external awarding and tin preview it in full screen. [23] Plug-ins are bachelor for Quick Look and so that you tin also view other files, such every bit Installer Packages.
- Safari 3, which includes Spider web Clip.
- Spaces , an implementation of virtual desktops (individually called "Spaces"), allows multiple desktops per user, with certain applications and windows in each desktop. [24] Users can organize sure Spaces for sure applications (e.chiliad., one for work-related tasks and one for entertainment) and switch between them. Exposé works inside Spaces, allowing the user to run into at a glance all desktops on 1 screen. [25] ) Users can create and command up to 16 spaces, and applications tin be switched between each one, creating a very large workspace. The car-switching feature in Spaces has annoyed some of its users. Apple added a new preference in x.5.2 which disabled this characteristic, but there were however bugs institute while switching windows. In 10.v.3, this problem was addressed and was no longer an result. [26]
- Spotlight incorporates additional search capabilities such as Boolean operators, every bit well as the ability to search other computers (with appropriate permissions). [27]
- Fourth dimension Machine , an automated backup utility which allows the user to restore files that have been deleted or replaced by another version of a file. [28] Though generally lauded in the press equally a stride forward for information recovery, Time Automobile has been criticized in multiple publications for lacking the capabilities of third-party backup software. Analyzing the feature for TidBITS, Joe Kissell pointed out that Time Auto does not create bootable copies of backed-up volumes, does not back upwards to AirPort Disk hard drives and will non support FileVault encrypted dwelling directories until the user logs out, concluding that the feature is "pretty good at what information technology does" only he volition only apply it as part of a "broader fill-in strategy". [29] [30] [31] One of these issues has been resolved, however; On March nineteen, 2008, updates were released for AirPort and Time Machine, allowing for Time Car to use a USB hard deejay which has been connected to an Aerodrome Extreme Base Station. [32]
- Universal Admission enhancements: significant improvements to applications including VoiceOver, along with increased support for Braille, airtight captioning and a new high‐quality Spoken language synthesis phonation. [33]
- Many changes to the user interface , such as a transparent carte bar, new icons, and a 3D Dock. Besides as this, the Apple tree icon is now blackness instead of blue. R.L. Prior, on the ThinkMac weblog, criticized a number of changes to Leopard's user interface, including the transparent menu bar and the new binder icons. [14] Decreased transparency of the card bar, along with the ability to disable the menu bar transparency were added with the 10.five.two release on February 11, 2008. [34]
- Russian language support, bringing the full to xviii languages. [35]
- Leopard removes support for Classic applications. [36]
- Introduced the Alex vocalism to VoiceOver .
Programmer technologies [ edit ]
- Native support by many libraries and frameworks for 64-bit applications, allowing 64-bit Cocoa applications. Existing 32-chip applications using those libraries and frameworks should continue to run without the need for emulation or translation. [37]
- Leopard offers the Objective-C 2.0 runtime, which includes new features such as garbage collection. Xcode 3.0 supports the updated language and was itself rewritten with information technology. [38]
- A new framework, Core Animation, allows a programmer to create complex animations while specifying only a "commencement" and a "goal" space. The main goal of Cadre Animation is to enable the creation of complex animations with pocket-size amounts of program lawmaking.
- Apple integrates DTrace from the OpenSolaris project and adds a graphical interface called Instruments (previously Xray). DTrace provides tools that users, administrators and developers can utilise to tune the performance of the operating system and the applications that run on it. [39]
- The new Scripting Bridge allows programmers to use Python 2.5 and Cherry-red 1.8.6 to interface with the Cocoa frameworks. [40]
- Ruby on Rails is included in the default install.
- Leopard'south OpenGL stack has been updated to version two.1, and uses LLVM to increase its vertex processing speed. [41] Apple has been working to become LLVM integrated into GCC; [42] LLVM's utilise within other operating system facilities has non been appear.
- The Graphics and Media State of the Union address confirmed many other features are possible because of Core Animation, such every bit live desktops, improvements to Quartz Composer with custom patches, a new PDF Kit for developers, and improvements to QuickTime APIs.
- The
FSEventsframework allows applications to annals for notifications of changes to a given directory tree. [43] - Leopard includes a read-simply implementation of the ZFS file system.
-
- In mid-December 2006, a pre-release version of Leopard appeared to include support for Sun'due south ZFS. [44] Jonathan Schwartz, CEO and President of Sun Microsystems, boasted on June half-dozen, 2007, that ZFS had go "the file system" for Leopard. [45] However, the senior project marketing director for Mac Os Ten stated on June 11, 2007, that the existing HFS+, non ZFS, would exist used in Leopard. Apple later on clarified that a read-simply version of ZFS would be included. [46]
- Leopard includes drivers for UDF 2.v, necessary for reading Hard disk DVD and Blu-ray discs using third-party drives, but the included DVD Histrion software can only play Hard disk DVDs authored by DVD Studio Pro. [47]
- Leopard includes a framework implementing latent semantic mapping for classifying (eastward.g. textual) data.
- Leopard is the first operating system with open source BSD code to be certified as fully UNIX-compliant. [48] [49] Certification means that software post-obit the Single UNIX Specification can be compiled and run on Leopard without the need for any code modification. [40] The certification only applies to Leopard when run on Intel processors. [49]
- Leopard includes J2SE 5.0. [50]
Security enhancements [ edit ]
New security features intend to provide better internal resiliency to successful attacks, in addition to preventing attacks from being successful in the kickoff place.
- Library Randomization
- Leopard implements library randomization, [9] which randomizes the locations of some libraries in retention. Vulnerabilities that corrupt program memory frequently rely on known addresses for these library routines, which allow injected code to launch processes or alter files. Library randomization is presumably a stepping-stone to a more complete implementation of address infinite layout randomization at a after engagement.
- Application Layer Firewall
- Leopard ships with two firewall engines: the original BSD IPFW, which was present in earlier releases of Mac OS X, and the new Leopard Application Layer Firewall. Unlike IPFW, which intercepts and filters IP datagrams earlier the kernel performs significant processing, the Application Layer Firewall operates at the socket layer, spring to individual processes. The Awarding Layer Firewall tin therefore make filtering decisions on a per-awarding basis. Of the two firewall engines, only the Application Layer Firewall is fully exposed in the Leopard user interface. The new firewall offers less control over private packet decisions (users can decide to allow or deny connections system-wide or to individual applications, just must utilise IPFW to fix fine-grained TCP/IP header-level policies). Information technology also makes several policy exceptions for system processes: neither mDNSResponder nor programs running with superuser privileges are filtered. [51]
- Sandboxes
- Leopard includes kernel-level support for function-based access control (RBAC). RBAC is intended to prevent, for example, an awarding similar Mail service from editing the password database.
- Application Signing
- Leopard provides a framework to use public cardinal signatures for code signing to verify, in some circumstances, that code has not been tampered with. Signatures can too be used to ensure that ane program replacing another is truly an "update", and conduct whatsoever special security privileges across to the new version. This reduces the number of user security prompts, and the likelihood of the user beingness trained to only clicking "OK" to everything.
- Secure Invitee Account
- Guests can exist given access to a Leopard system with an business relationship that the system erases and resets at logout. [52]
Security features in Leopard accept been criticized every bit weak or ineffective, with the publisher Heise Security documenting that the Leopard installer downgraded firewall protection and exposed services to attack fifty-fifty when the firewall was re-enabled. [53] [54] Several researchers noted that the Library Randomization feature added to Leopard was ineffective compared to mature implementations on other platforms, and that the new "secure Guest account" could be abused by Guests to retain access to the arrangement even after the Leopard log out process erased their home directory. [55] [56]
System requirements [ edit ]
Apple states the following bones Leopard system requirements, although, for some specific applications and features (such as iChat backdrops) an Intel processor is required: [57]
- Processor: any Intel processor, or PowerPC G5 or G4 (867 MHz and faster) processor
- Optical drive: internal or external DVD drive (for installation of the operating arrangement)
- Memory: minimum 512 MB of RAM (additional RAM (one GB) is recommended for evolution purposes)
- Difficult drive chapters: Minimum 9 GB of disk space available.
Leopard's retail version was not released in separate versions for each blazon of processor, merely instead consisted of one universal release that could run on both PowerPC and Intel processors. [37] Withal, the install discs that send with Intel-based Macs simply contain Intel binaries.[ commendation needed ]
Processor type and speed are checked during installation and installation halted if insufficient; still, Leopard will run on slower G4 processor machines (e.m., a 733 MHz Quicksilver) if the installation is performed on a supported Mac and its difficult drive and so moved to a slower/unsupported 1 (the bulldoze may either be an internal mechanism or a Firewire external).[ commendation needed ]
Supported machines [ edit ]
Leopard can run on the later apartment-panel iMac G4s, the iMac G5, iMac Intel Core Duo and iMac Intel Core 2 Duo, PowerBook G4, Power Mac G4, Power Mac G5, iBook G4, MacBook, MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, Mac Pro, Mac Mini, Xserve, Xserve G5, Xserve RAID, Macintosh Server G4, and subsequently eMac models. Leopard tin run on older hardware as long as they take a G4 upgrade installed running at the 867 MHz or faster, have at least 9 GB free of hard bulldoze space, 512 MB RAM and have a DVD bulldoze. Leopard still will not run on the 900 MHz iBook G3 models fifty-fifty though they exceed the minimum 867 MHz requirement. This is due to the lack of AltiVec support in the G3 line of processors. Leopard can be "hacked" (see below) to install on these G3 and pre-867 MHz G4 machines but the system may carry erratically and many of the programs, features, and functions may not work properly or at all. Every bit of mid-2010, some Apple computers have firmware mill installed which will no longer allow installation of Mac Bone Ten Leopard. These computers just allow installation of Mac Os Ten Snow Leopard.[ citation needed ] However, some computers (such as the 2011 model of the Mac mini) can accept Leopard installed on them without hacking.[ citation needed ]
Usage on unsupported hardware [ edit ]
Some ways of running Leopard on sure unsupported hardware, primarily PowerPC G4 computers with CPU speeds lower than the official requirement of 867 MHz, accept been discovered. A common mode is utilise of the plan LeopardAssist, which is a bootloader similar in some respects to XPostFacto (used for installing earlier releases of Mac Os X on unsupported G3 and pre-G3 Macs) that uses the Mac'southward Open Firmware to tell Leopard that the machine does have a CPU meeting the 867 MHz minimum requirement that the Installer checks for earlier installation is allowed to embark, when in reality the CPU is slower. [58] Currently, LeopardAssist simply runs on slower G4s and many people have installed Leopard successfully on these older machines.
Users who have admission to supported hardware have installed Leopard on the supported motorcar then simply moved the hard drive to the unsupported automobile. Alternatively, the Leopard Installation DVD was booted on a supported Mac, then installed on an unsupported Mac via Firewire Target Disk Mode. Leopard is only compiled for AltiVec-enabled PowerPC processors (G4 and G5) though, as well as Intel, then both of these methods will only work on Macs with G4 or later CPUs. While some of the earlier beta releases were made to run on some afterwards G3 machines (mostly later 800–900 MHz iBooks), no success with the retail version has been officially reported on G3 Macs except for some later iMacs and "Pismo" PowerBook G3s with G4 processor upgrades installed.
For a number of months afterwards Leopard'due south release it appeared that the simply G3 Macs on which Leopard could be run were those with both an aftermarket G4 processor and an AGP graphics carte, equally failures with the OS partially booting before crashing were reported on older Macs such every bit the original tray-loading iMacs and the Beige and Blue & White Power Mac G3 (all with G4 upgrades as Leopard will not fifty-fifty begin to load without one) whereas information technology would boot fine on newer Macs where the Installer restriction had been circumvented. However, more recently it has been reported [59] [60] that with some more than work and use of kernel extensions from XPostFacto, Tiger and beta builds of Leopard, the OS can be made to run on G4-upgraded Macs as old as the Power Macintosh 9500, despite the lack of AGP-based graphics. While Leopard can be run on any Mac with a G4 or later processor, some functionality such every bit Front Row or Time Machine fails to work without a Quartz Extreme-capable graphics card, which many of the earlier G4s did not include in their factory specification.
Since Apple moved to using Intel processors in their computers, the OSx86 customs has developed and now besides allows Mac OS X Tiger and subsequently releases to exist installed and run successfully on non-Apple x86-based computers, admitting in violation of Apple tree's licensing understanding for Mac OS 10.
Packaging [ edit ]
The retail packaging for Leopard is significantly smaller than that of previous versions of Mac Os 10 (although afterwards copies of Tiger besides came in the new smaller box). Information technology also includes a lenticular encompass, making the X announced to float to a higher place a imperial galaxy, somewhat resembling the default Leopard desktop wallpaper. [61]
Release history [ edit ]
| Version | Build | Date | Os proper noun | Notes | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ten.five | 9A581 | October 26, 2007 | Darwin ix.0 xnu-1228~ane | Original retail DVD release | N/A |
| 10.5.1 | 9B18 | November 15, 2007 | Darwin 9.1 xnu-1228.0.ii~1 | About the Mac Bone X x.5.1 Update; 2nd retail DVD release | Mac Os Ten 10.5.1 Update |
| 9B2117 | December 14, 2007 | Darwin 9.i.1 | Forked build for Early 2008 Mac Pro and Xserve | ||
| 10.5.two | 9C31 | February xi, 2008 | Darwin 9.2 xnu-1228.3.13~1 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.ii Update | Mac Os X 10.5.2 Philharmonic Update |
| 9C7010 | Darwin ix.2 | ||||
| 10.5.3 | 9D34 | May 28, 2008 | Darwin 9.3 xnu-1228.5.18~one | About the Mac Bone Ten 10.five.three Update | Mac OS X 10.v.3 Update |
| x.5.four | 9E17 | June 30, 2008 | Darwin 9.4 xnu-1228.v.20~1 | Near the Mac Os X 10.five.four update; Third retail DVD release | Mac Bone 10 x.5.4 Update |
| 10.5.5 | 9F33 | September xv, 2008 | Darwin 9.5 1228.7.58~i | About the Mac Os X 10.v.v Update | Mac OS 10 10.v.five Update |
| 10.5.half dozen | 9G55 | December 15, 2008 | Darwin ix.6 | Most the Mac Os X x.v.6 Update | Mac Os 10 10.5.six Update |
| 9G66 | Jan six, 2009 | Fourth retail DVD release (function of Mac Box Set) | Northward/A | ||
| 9G71 | Northward/A | Darwin 9.6 xnu-1228.ix.59~1 | N/A | ||
| x.5.7 | 9J61 | May 12, 2009 | Darwin nine.vii xnu-1228.12.xiv~ane | Most the Mac OS X 10.v.seven Update | Mac OS 10 10.5.7 Update |
| 10.5.8 | 9L30 | August 5, 2009 | Darwin 9.8 | About the Mac Os X ten.5.8 Update | Mac Bone Ten 10.5.8 Update |
| 9L34 | August 31, 2009 | Darwin 9.8 xnu-1228.15.4~1 | Mac Bone X Server 10.five.8 Update v.1.1 | Due north/A | |
Compatibility [ edit ]
After Leopard'southward release, in that location were widely reported incidents of new Leopard installs hanging during kick on the blue screen that appears just earlier the login process starts. [62] Apple attributed these problems to an outdated version of an unsupported add-on extension called Awarding Enhancer (APE), from Unsanity which had been incompatible with Leopard. Some users were unaware that APE had been silently installed during installation of Logitech mouse drivers. However, only the users who did not have the latest version of APE installed (2.0.3 at that time) were affected. [63] Apple published a knowledge base article on how to solve this problem. [64]
Google announced that the Chrome browser will be dropping back up for Leopard starting with Chrome 21. By that time Chrome volition no longer auto-update, and new Chrome installations are not allowed. Their rationale for removal of back up is that Leopard is an "OS X version also no longer being updated by Apple." [65]
Firefox also dropped back up for Leopard afterward it shipped Firefox 16 in October 2012. [66] TenFourFox is a port of Firefox for the PPC architecture, released after Firefox dropped back up for Leopard.
References [ edit ]
- ^ "Mac OS X Version ten.5 on Intel-based Macintosh computers". The Open Group. Archived from the original on May 11, 2008. Retrieved December 4, 2014.
- ^ a b "Apple to Ship Mac OS 10 Leopard on October 26". Apple tree Inc. Oct 16, 2007.
- ^ Johnson, Jeff (September 1, 2009). "Apple hot-swapped Mac Bone X 10.5.8". Lap Cat Software Weblog. Archived from the original on Feb one, 2016. Retrieved August vii, 2014.
- ^ "Nearly the Mac OS X v10.5.8 Update". Apple Inc.
- ^ "SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT FOR MAC OS Ten Single Utilize, Family Pack and Leopard Upgrade Licenses for use on Apple-branded Systems" (PDF). apple.com. Apple Inc. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 25, 2015. Retrieved March 19, 2015.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (December 17, 2013). "Apple signals end to Os X Snowfall Leopard support". Computerworld. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014.
Apple provided the last update to Leopard in June 2011
- ^ "Apple retires Snow Leopard from support, leaves i in five Macs vulnerable to attacks". February 26, 2014. Archived from the original on May 28, 2014. Retrieved May 9, 2014. See the graph picture on the web
- ^ "Apple Announces Mac Os X Server Leopard" (Press release). Apple Inc. Oct 16, 2007.
- ^ a b c d "Mac OS X Leopard — Features - 300+ New Features". Apple Inc. October sixteen, 2007. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007. Retrieved Oct 16, 2007.
- ^ "Apple'south Intel switch: Jobs' keynote transcript". CNet. June 15, 2005. Retrieved April 12, 2007.
- ^ a b Ryan Block (August vii, 2006). "Live from WWDC 2006: Steve Jobs keynote". Engadget. Archived from the original on August xiii, 2006. Retrieved August 7, 2006.
- ^ Apple Inc. (April 12, 2007). "Apple Statement" (Printing release). Yahoo! Finance. Archived from the original on April 14, 2007. Retrieved April 12, 2007.
- ^ Apple tree Inc. "Leopard Sneak Peek — Dashboard". Archived from the original on November sixteen, 2006. Retrieved November 28, 2006.
- ^ a b Rory Prior (October 28, 2007). "ThinkMac Blog: Leopard stupidity". Archived from the original on Apr 20, 2009.
- ^ "Non-mentioned Leopard features". Archived from the original on Oct eleven, 2007. Retrieved October ane, 2007.
- ^ Apple Inc. "Leopard Sneak Peek — iCal". Archived from the original on April 7, 2007. Retrieved April 23, 2007.
- ^ "WWDC 2006 Keynote — Live Coverage" . Retrieved August 7, 2006.
- ^ Apple Inc. "Leopard Sneak Peek — iChat". Archived from the original on November 27, 2006. Retrieved November 28, 2006.
- ^ Apple Inc. "Leopard Sneak Peek — Postal service". Archived from the original on November 27, 2006. Retrieved November 28, 2006.
- ^ Glenn Fleishman (October 25, 2007). "Leopard Simplifies Sharing". TidBITS. Archived from the original on October 27, 2007. Retrieved Oct 26, 2007.
- ^ Apple tree Inc. "Mac OS X — Leopard Sneak Peek". Apple. Archived from the original on August 13, 2006. Retrieved Baronial eight, 2006.
- ^ Apple tree Insider. "Road to Mac OS X Leopard: an extensive look at Preview 4.0". Archived from the original on October 3, 2007. Retrieved October 4, 2007.
- ^ Apple tree Inc. "Quick Wait". Apple. Archived from the original on August ix, 2007. Retrieved April 11, 2006.
- ^ Apple tree Inc. "Leopard Sneak Peek — Spaces". Archived from the original on July 10, 2007. Retrieved November 28, 2006.
- ^ "Bone 10.5 Leopard Spaces + Exposé". GoogleVideos. GoogleVideos. 2006. Archived from the original on Jan 17, 2007. Retrieved Baronial 28, 2006.
- ^ "Why Apple tree Spaces is broken". Blogs.sun.com. Archived from the original on Baronial nineteen, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Rob Griffiths (August 15, 2006). "Leopard outset looks: Spotlight". Macworld. Archived from the original on April 27, 2007. Retrieved Apr 12, 2007.
- ^ Rob Griffiths (Baronial 9, 2006). "WWDC: Apple's Time Machine looks to ease backups". Computerworld Inc. Archived from the original on October xiv, 2007. Retrieved Apr 12, 2007.
- ^ Kissell, Joe (October 28, 2007). "TidBITS Macs & Mac Os X: Time Machine: The Good, the Bad, and the Missing Features". Db.tidbits.com. Archived from the original on June 8, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Jason Snell (October 26, 2007). "Leopard is an upgrade that roars". Archived from the original on February thirteen, 2016.
- ^ Ihnatko, Andy. "What'southward Leopard really worth?". Macworld. Archived from the original on May 20, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "Update allows Time Auto backups on Aerodrome Extreme". Macworld. March twenty, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2020.
- ^ Apple tree Inc. "Leopard Sneak Peek — Accessibility". Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved November 28, 2006.
- ^ "Information well-nigh the x.five.2 update". Docs.info.apple tree.com. May two, 2008. Archived from the original on March 15, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Apple Inc. "Apple — Mac OS Ten Leopard — Technical Specs". Apple.com. Archived from the original on December 2, 2008. Retrieved November four, 2008.
- ^ "Practise Archetype applications piece of work with Mac OS X ten.5 or Intel-based Macs?". Knowledge Base. Apple Inc. Jan xiii, 2006. Archived from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved Oct 25, 2007.
- ^ a b Apple Inc. "Mac OS 10 — Leopard Sneak Peek". Apple. Archived from the original on September half-dozen, 2007. Retrieved Baronial 8, 2006.
- ^ Apple Inc. "Mac Os X Leopard Sneak Peek — Xcode iii.0". Apple. Archived from the original on June 29, 2007. Retrieved Baronial 7, 2006.
- ^ Mike Shapiro (Baronial seven, 2006). "DTrace on Mac Bone X at WWDC". weblog. Archived from the original on August 13, 2006. Retrieved August 8, 2006.
- ^ a b "Mac Os 10 Leopard — Engineering science — UNIX". Apple. Archived from the original on August 23, 2007. Retrieved June 11, 2007.
- ^ Lattner, Chris (August 15, 2006). "A cool apply of LLVM at Apple: the OpenGL stack". LLVMdev. Archived from the original on Nov 4, 2006. Retrieved August 21, 2006.
- ^ Siracusa, John (December four, 2005). "Avoiding Copland 2010: Hints of things to come?". FatBits. Archived from the original on June 24, 2006. Retrieved Baronial 8, 2006.
- ^ "Leopard Technology Series for Developers: OS Foundations". October 26, 2007. Archived from the original on May 9, 2008. Retrieved August 21, 2008.
- ^ World of Apple (December 17, 2006). "ZFS Makes information technology to Leopard". Globe of Apple. Archived from the original on May 16, 2007. Retrieved Dec 17, 2006.
- ^ Schwartz, Jonathan (June 6, 2007). "Washington D.C. Sun Conference". sun.com. Archived from the original on June 7, 2007. Retrieved June 6, 2007.
- ^ Gonsalves, Antone. "Apple Says No Lord's day File Organization For Leopard". InformationWeek. Archived from the original on June 14, 2007. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ "DVD Player: Plays HD DVD discs authored in DVD Studio Pro only". Apple. Archived from the original on Dec 29, 2007. Retrieved December 12, 2007.
- ^ "Mac Os X Leopard Achieves UNIX 03 Product Standard Certification". The Open up Group. November 19, 2007. Archived from the original on July v, 2008.
- ^ a b "The Open Brand - Register of Certified Products (entry for Mac Os 10 10.v)". The Open Grouping. May 18, 2007. Archived from the original on May 11, 2008. Retrieved February 21, 2013.
- ^ "Coffee Frequently Asked Questions". developer.apple tree.com. Archived from the original on August four, 2010. Retrieved June nine, 2010.
- ^ "Mac Bone X 10.5 Leopard: About the Application Firewall". Docs.info.apple.com. May 19, 2010. Archived from the original on April xviii, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Mogull, Rich (October 22, 2007). "TidBITS Safe Calculating: How Leopard Will Improve Your Security". Db.tidbits.com. Archived from the original on June viii, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ Lisa Vaas (October 30, 2007). "Leopard Has More Holes than Spots". Eweek.
- ^ Jürgen Schmidt (October 29, 2007). "A second look at the Mac Bone X Leopard firewall" . Retrieved Oct 7, 2020.
- ^ "Quick Leopard Update". Securosis. October 29, 2007. Retrieved October seven, 2020.
- ^ "Matasano Chargen » What We've Since Learned Near Leopard Security Features". Jan 11, 2008. Archived from the original on January 11, 2008.
- ^ Apple Inc. "Mac OS 10 Leopard- Technical Specs". Apple. Archived from the original on March 19, 2008. Retrieved Baronial 31, 2009.
- ^ LeopardAssist — Install Leopard on Sub-867MHz[sic] Macs Archived Apr 3, 2008, at the Wayback Car
- ^ "Opera Trumps Safari, Flashed Video Cards for Macs, Hacking Leopard for G3 Power Macs, and More". Lowendmac.com. January 16, 1986. Archived from the original on June 11, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "Leopard running on a Beige G3". Youtube.com. Baronial 25, 2008. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ arn. "Mac Os X 10.5 Leopard Packaging". Archived from the original on October 26, 2007. Retrieved October 25, 2007.
- ^ Krazit, Tom (October 28, 2007). "Apple acknowledges some Leopard installation problems". News.cnet.com. Archived from the original on June 24, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "Blue in the Face". Daring Fireball. October 29, 2007. Archived from the original on June 14, 2011. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "Mac OS X 10.5: "Blue screen" appears afterwards installing Leopard and restarting". Docs.info.apple.com. Oct 30, 2008. Archived from the original on April 18, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2011.
- ^ "Chrome no longer supports Mac OS X 10.5". Archived from the original on Nov x, 2012.
- ^ "Mozilla sets end of Firefox for OS 10 Leopard". Macworld. Archived from the original on Nov 17, 2015. Retrieved Nov fifteen, 2015.


Comments
Post a Comment